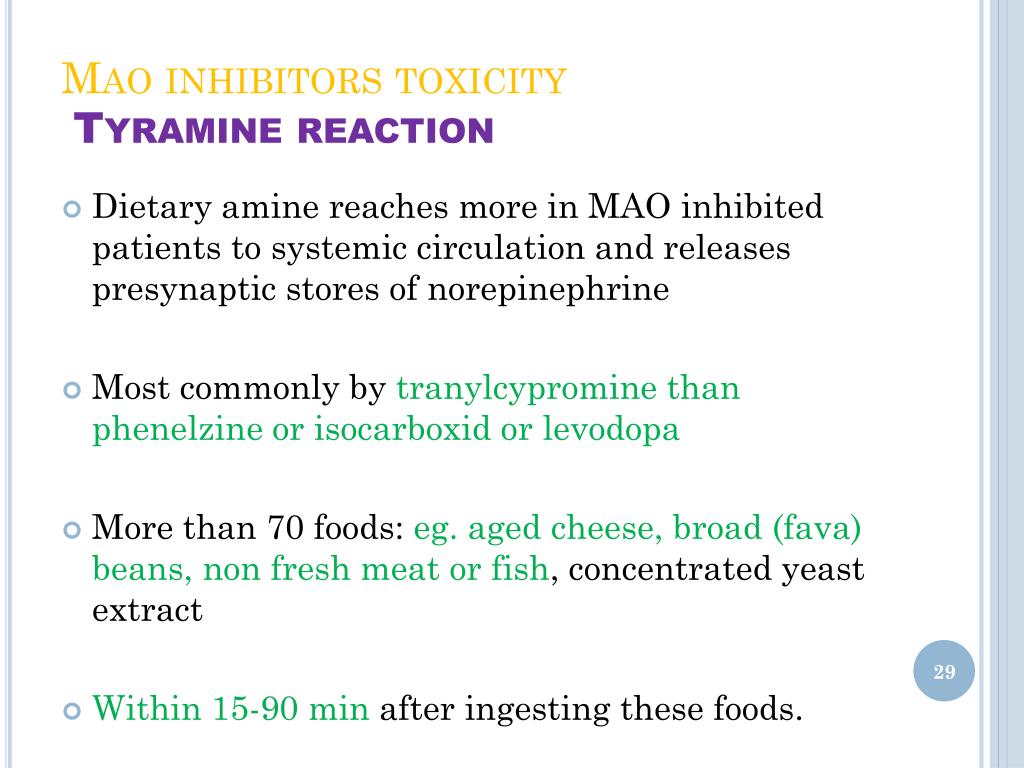
0406 · Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are a class of drugs primarily used as antidepressants Their use has waned over the last several decades due to the availability of other medications for depression, their side effects, and their interactions with food and drugs (which may require a special diet by those who take them) 1 However, they are still used to treat some cases ofA reaction is an increase of BP over 30 60 minutes and usually shows first as a forceful thumping heartbeat Pulse usually becomes slower 13 If blood pressure goes up to 180 mm Hg or more severe headache is usualC'est le cas, entre autres, pour une substance appelée la tyramine Les utilisateurs de médicaments de la famille des inhibiteurs de la monoamineoxydase (IMAO) ou de médicaments ayant des propriétés similaires n'éliminent plus normalement cette substance Un excès de tyramine risque de provoquer une crise hypertensive très nocive On leur suggère alors d'éviter les aliments qui
Moclobemide Wikiwand
Why avoid tyramine with maoi
Why avoid tyramine with maoi-React with tyramine, a chemical present in some foods, causing your blood pressure to rise There are two types of MAOI medicines; · So while you are taking MAOIs for depression, Dr Edlund explains, your body is already working harder to process naturally occurring tyramine Any tyramine that comes from your diet is "extra," and can easily accumulate in your body and overload the system That's what causes side effects such as headaches and elevated blood pressure, as well as gastrointestinal



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Osmosis
Reports of hypertensive reactions from monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) began to proliferate in the early 1960s Asatoor did extensive research and found that the combination of an MAOI and a food containing tyramine resulted in the hypertensive interaction ("the cheese reaction") Because of the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage and death, clinicians were hesitant toIf excessive tyramine is ingested the blood pressure typically starts to increase from about half an hour after ingestion (sooner for liquids on an empty stomach), and remains elevated for 12 hours the magnitude and duration of that elevation is dose related, so unless a large amount of tyramine has been ingested ( mg) the reaction will be shortlived (about one hour)Six milligrams of tyramine is sufficient to elicit a mild reaction in people taking MAOI and 1025 milligrams can cause a severe reaction This can lead to a sudden spike in blood pressure, and to stroke, brain hemorrhage and death Tintinalliâ s Emergency Medicine A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e However,, The two drugs are not interchangeable nor dose equivalents Tyramine
Tyramine is a natural compound found in plants and animals It is a byproduct of the breakdown of tyrosine, an amino acid Tyrosine and tyramine are commonly found in1004 · MAOI popularity has diminished over the years mostly due to safety concerns about the tyramine reaction and hypertensive crisis known as the "Cheese effect" Essentially, there is the possibility that some foods, especially aged cheese, may cause a potentially fatal blood pressure reaction when combined with these drugs However, there is some debate in the2702 · MAOI toxicity can occur in the following three ways Drugfood interactions the socalled tyramine reaction Overdose Drugdrug interactions All three mechanisms produce similar symptoms and signs, which stem from an excess of catecholaminergic neurotransmitters (see Pathophysiology
Diet advice when taking MAOI and foods containing tyramineMAOI unavailability Act now Spread this open letter by international MAOI experts https//psychA large dietary intake of tyramine (or a dietary intake of tyramine while taking MAO inhibitors) can cause the tyramine pressor response, which is defined as an increase in systolic blood pressure of 30 mmHg or moreMAOI medicines belong to a group of medicines called antidepressants that are used to treat depression They can react with tyramine, a chemical present in some foods, causing your blood pressure to rise There are two types of MAOI medicines;



Maoi Drugs News
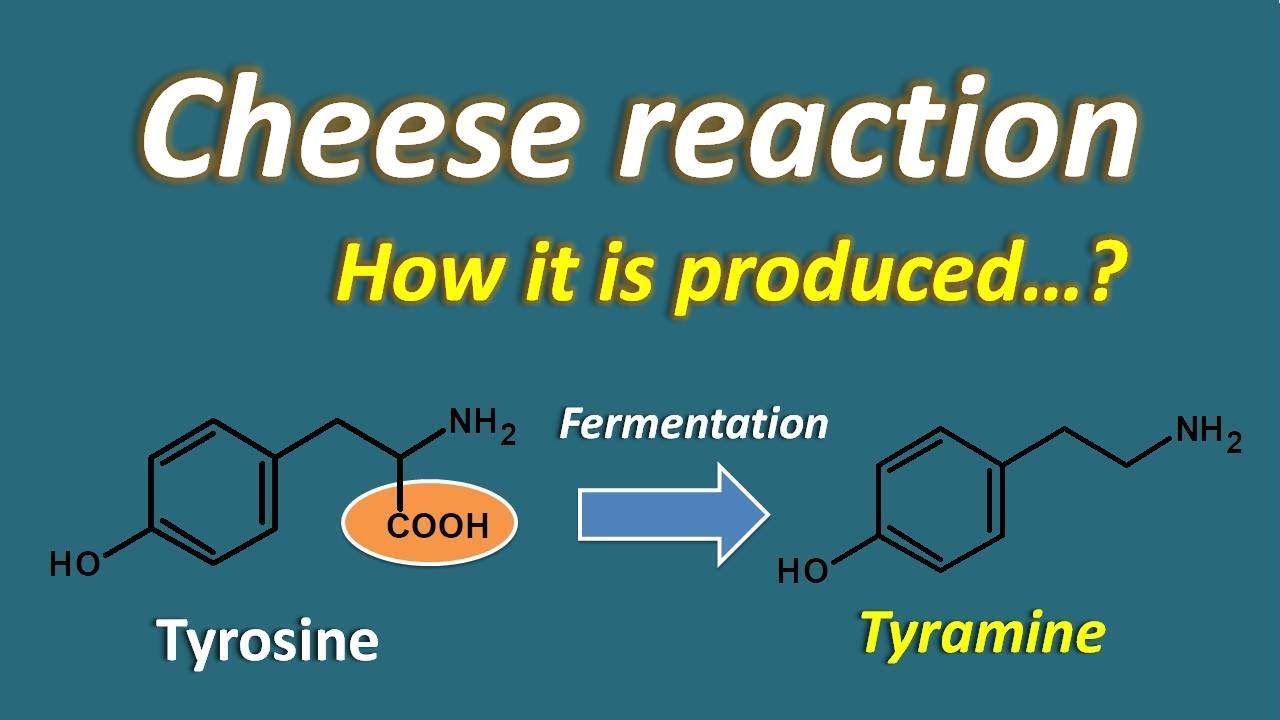


Cheese Reaction How It Is Produced Youtube
Tyramine elicited, after oral administration (by gavage), a statistically significant dosedependent increase in blood pressure from the dose of 10 mg/kg in solution (ie 23 / 3 mm Hg, N = 36) and 40 mg/kg in feed preparation (ie, / 2 mm Hg, N = 26) Almost all rats showed a systolic blood pressor increase higher than 30 mm Hg after oral administration of tyramine at a dose of 80 mg1919 · MAOIs can cause dangerous interactions with certain foods and beverages You'll need to avoid foods containing high levels of tyramine ― an amino acid that regulates blood pressure ― such as aged cheeses, sauerkraut, cured meats, draft beer and fermented soy products (for example, soy sauce, miso and tofu) · MAOI and Tyramine Reaction FORUM FOR PSYCHIATRY RESIDENTS Psychiatry PsychiatryNeurologyPsychology discussion PsychoPharmacology Page 1 of 1



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download
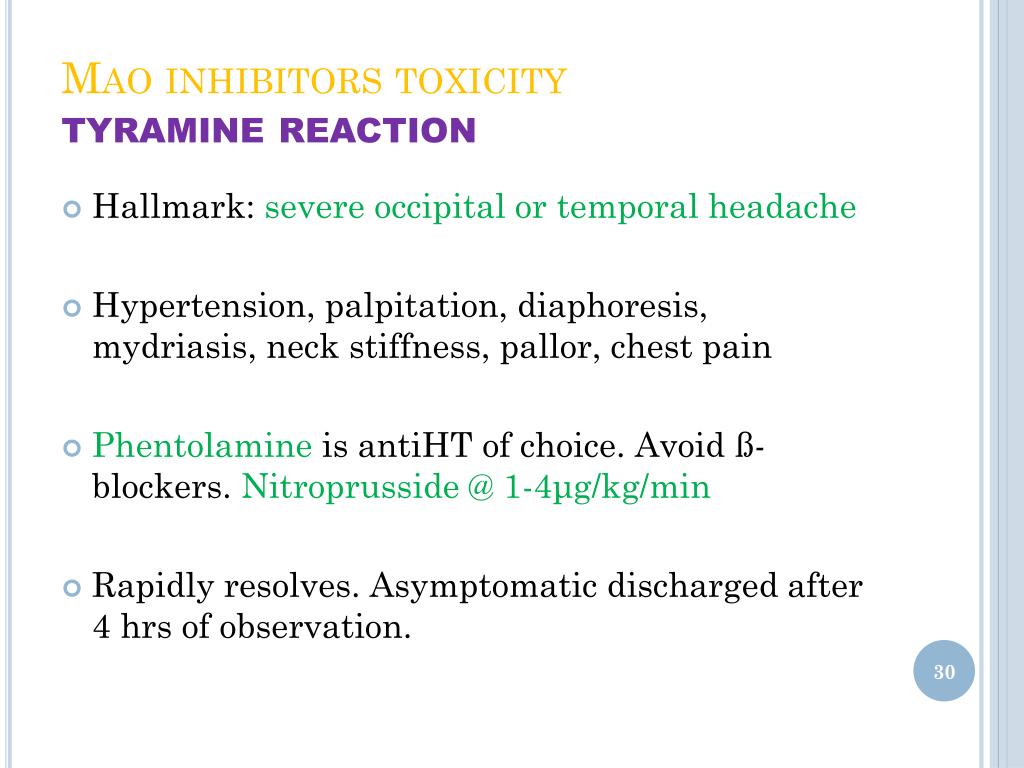
Response to tyramine ('cheese reaction'), is serotonin toxicity (ST)— aka serotonin syndrome That is now well defined and is straightforward to avoid by not coadministering any drug with serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) potency There are no therapeutically used drugs, other than drugs with SRI activity, that are capable of inducing serious ST with MAOIs Anaesthesia is notRecently, confidence in handling such reactions and in MAOI usage has increased MAOIs treat anxiety and depression by supposedly inhibiting the inactivation of neurotransmitters A side effect is the concurrent failure to inactivate the potent vasopressor amine, tyramine Consumption of 6 mg of tyramine may produce a mild crisis whereas 10 to 25 mg may produce severe headachesResponse to tyramine ('cheese reaction'), is serotonin toxicity (ST) — aka serotonin syndrome That is now well defined and is straightforward to avoid by not co administering any drug with serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) potency There are no therapeutically used drugs, other than drugs with SRI activity, that are capable of inducing serious ST with MAOIs Anaesthesia is not


Ppt Management Of Specific Drug Poisoning Antidepressants Barbiturates Powerpoint Presentation Id



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Sympathomimetics In Malayalam Youtube
· An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that(1) Certain foods should be avoided while on this class medicationspecifically tyramine containing foods High tyramine containing foods can actually cause dangerous spikes in blood pressure while taking a MAOI Corned beef is considered a cured beef product Other cured meats include dry summer sausage and salamiSimilarly, taking a MAOI with foods like cheese, which is high in tyramine, is dangerous because the inhibition of the MAOA enzyme causes a dangerous elevation of serum tyramine levels, which can lead to hypertensive symptoms However, selectively inhibiting only the MAOB enzymes may bypass this problem, because MAOB mostly metabolizes dopamine If MAOB is inhibited, then



Psychopharmacology Part 1 Antidepressants And Anxiolytics Ppt Download


Frontiers Monoamine Oxidases Maos As Privileged Molecular Targets In Neuroscience Research Literature Analysis Molecular Neuroscience
Chain Tyramine increase has a lot to do with 'freshness' (ie time and storage conditions) Symptoms of Blood Pressure Reactions?MAOIs occasionally react with tyraminerich foods or a variety of other medicines to cause severe hypertension, excruciating headache, and sometimes a subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhage – a hypertensive crisis This iatrogenic catastrophe, classically associated with MAOI antidepressants, is not peculiar to their use For example, MAOIs used in Parkinson disease treatment, such as · In reply to Re MAOI Reaction Symptoms , posted by Jennifer on June 10, 00, at Dear Jennifer, Thank you for contributing such a great post I hadn't known that the MAOItyramine reaction could take such a delayed and gradual course You know more about this reaction than anyone I have encountered, and this is very important information



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Moclobemide Wikiwand
· Tyramine causes hypertensive crises after MAO inhibition aka the "cheese effect" or "cheese crisis" Using a MAO inhibitor (MAOI), the intake of approximately 10 to 25 mg of tyramine is required for a severe reaction compared to 6 to 10 mg for a mild reaction Tyramine rich food should also be avoided by people prone to headache and migraineBut tyramine can reach dangerous levels if you eat foods containing tyramine while on an MAOI This can lead to a sudden spike in blood pressure, and to stroke, brain hemorrhage and death There have been nearly 100 deaths recorded due to interaction between pharmaceutical MAOIs and tyraminecontaining foods However, Ayahuasca is a reversible MAOI, or RIMA RIMAs are notThe older types (isocarboxazid, phenelzine and tranylcypromine) can provoke a more severe reaction with tyramine containing foods The


Ppt Management Of Specific Drug Poisoning Antidepressants Barbiturates Powerpoint Presentation Id



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry
If you take an MAOI and you eat hightyramine foods, tyramine can quickly reach dangerous levels This can cause a serious spike in blood pressure and require emergency treatment Avoid consuming foods that are high in tyramine if you take an MAOI You may need to continue following a lowtyramine diet for a few weeks after you stop the medicationReports of hypertensive reactions from monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) began to proliferate in the early 1960s Asatoor did extensive research and found that the combination of an MAOI and a food containing tyramine resulted in the hypertensive interaction ("the cheese reaction") Because of the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage and death, clinicians were hesitant to use the MAOIsHigh levels of tyramine in the body can lead to an increase inyour blood pressure This is This is an immediate effect of consuming tyramine in large quantities and can cause unpleasant



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Osmosis
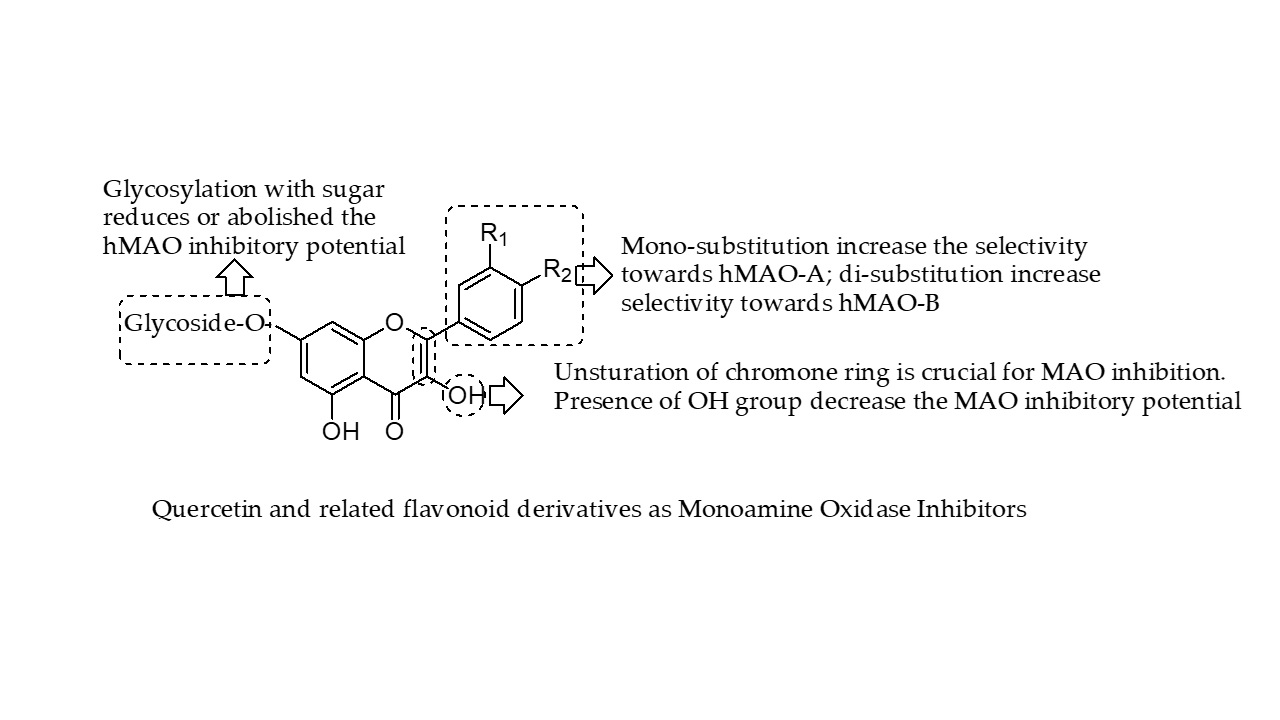


Molecules Free Full Text Quercetin And Related Chromenone Derivatives As Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Targeting Neurological And Mental Disorders Html
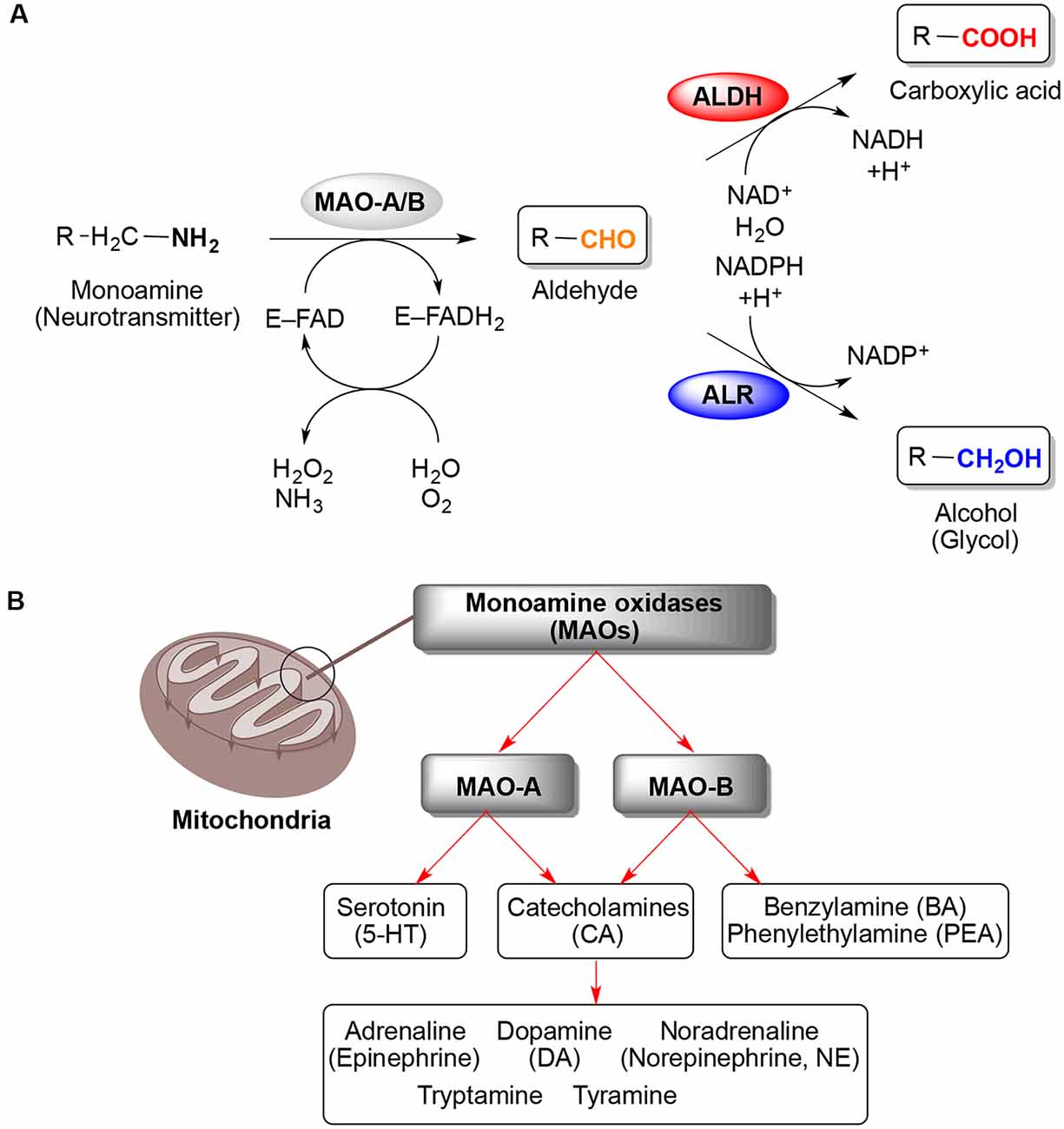
Tyramine = a monoamine This substance indirectly increases release of catecholamines The enzyme monoamine oxidase naturally breaks down tyramine and other monoamine chemicals MAOIs blocks this breakdown pathway, increasing levels of tyramine and thereby increasing catecholamines such as norepinephrineFoods high in tyramine, "the decarboxylated product of the amino acid tyrosine"1, can cause a hypertensive crisis when on MAOI therapy A hypertensive crisis is also known as dangerously high blood pressure which can lead to stroke and even death Blood pressure readings during a hypertensive crisis are higher than 180/110 mmHgA newer MAOI that is currently being studied called moclobemide may have a lower risk of triggering hypertensive reactions Further, a transdermal (skin patch) formulation called selegiline that considerably reduces the risk of tyramine reaction and lessens the dietary restrictions of MAOI treatment, has recently been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)



Safinamide Wikidoc



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
TyramineInduced Hypertension Crisis Tyramine is a compound found in many foods This compound has an effect on blood pressure and is regulated by the MAO enzyme When the MAO enzyme is inhibited (for instance, when you take an MAOI), tyramine can reach dangerously high levels, resulting in critically high blood pressure · Tyramine side effects Avoid consuming foods that are high in tyramine if you take monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) for depression You may need to continue following a lowtyramine diet for a few weeks after you stop the medication Tyramine has an effect on blood pressure and is regulated by the enzyme monoamine oxidaseTyramine is a dietary amine similar to amphetamine normally metabolized by MAO Tyramine is a monoamine and acts indirectly to release catecholamines Tyramine is typically metabolized by monoamine oxidase in the gut, a process that MAOIs interfere with Tyramine is found in preserved meat, fish, cheese, alcohol, and proteinrich foods which are



Anti Depressants Benzodiazepine Antidepressant
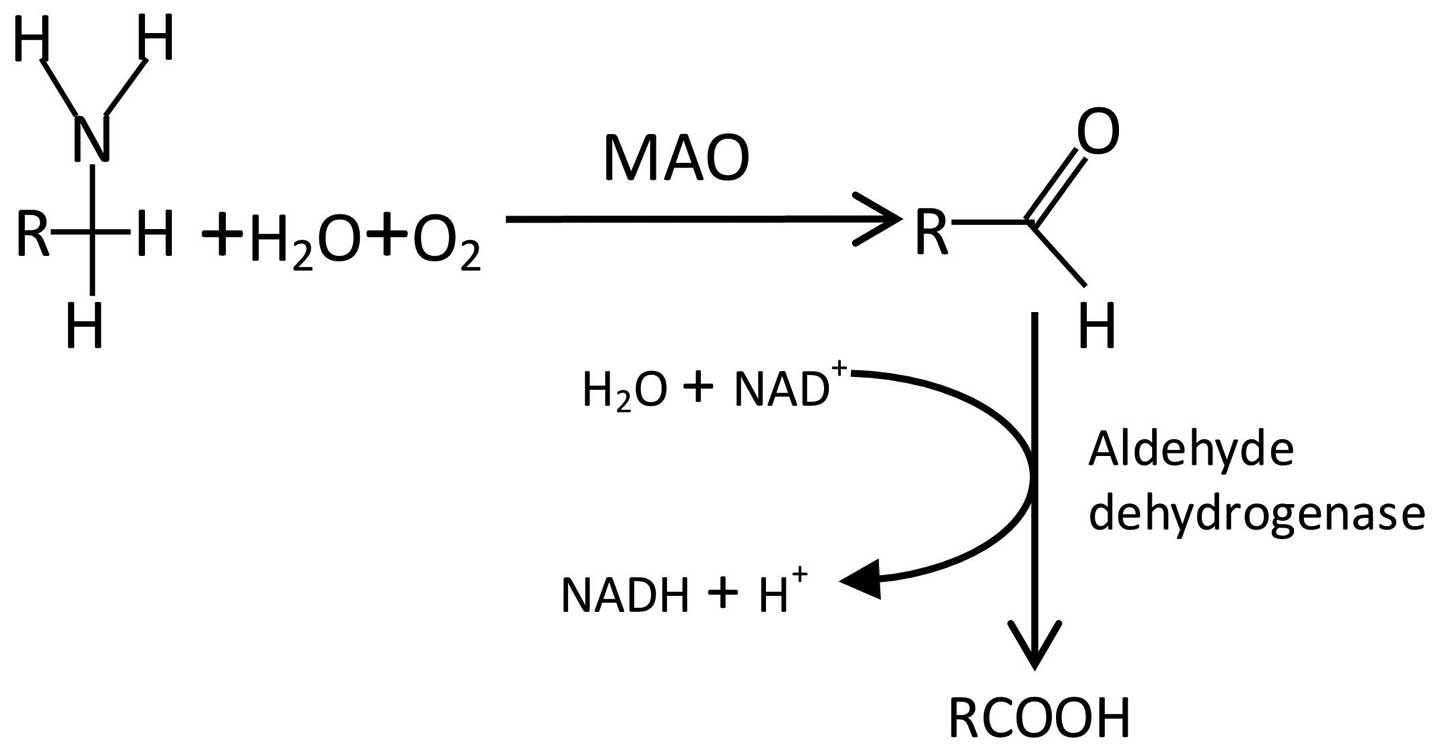


Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Promising Therapeutic Agents For Alzheimer S Disease Review
Tyramine is a pressor agent (ie increases blood pressure) and is normally metabolized by MAOA in the gut and the liver If an individual takes both an MAOI and eats foods with high tyramine content, tyramine levels can quickly reach dangerous and cause a hypertensive crisis that requires emergency treatment (see History and Mechanism of Action section above)It has i ndirect sympathomimetic action causing the release of stored catecholaminesPlease review the dietary restrictions that should be observed when a patient is receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) therapy A Tyramine is an amino acid which is found in various foods and is an indirect sympathomimetic that can cause a hypertensive reaction in patients receiving MAOI therapy



Influence Of Phenolic Compounds And Mao Inhibitors Or Ssao Inhibitors Download Scientific Diagram



Cydap A Fluorescent Probe For Cytosolic Dopamine Detection Biorxiv
The tyraminecheese reaction, hypertensive crises, and MAOI diets The amino acid tyrosine (from the Greek word for cheese, tyros) was isolated from cheese as early as 1846 By 1911, it was known that tyramine (derived from tyrosine) had the potential to increase blood pressure However, it was a series of case reports in the 1960s that described hypertensive crises associated with MAOIsMAOIs and the cheese reaction B ecause gastrointestinal monoamine oxidase (MAO) effectively prevents dietary pressor amines, typically tyramine, from entering the tissues, a marked hypertensive response (the "cheese reaction") can occur when subjects treated with antidepressant MAO inhibitors ingest foods or beverages rich in such aminesThe older types (isocarboxazid, phenelzine and tranylcypromine) can provoke a more severe reaction with tyramine containing foods The newer reversible MAOI medicine, moclobemide is less likely to cause a severe



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Revisiting A Therapeutic Principle


Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Wikipedia
· Six milligrams of tyramine is sufficient to elicit a mild reaction in people taking MAOI and 1025 milligrams can cause a severe reaction SA Tailor, et al published a paper in 1994 entitled, "Hypertensive episode associated with phenelzine and tap beer—a reanalysis of the role of pressor amines in beer"MECHANISM Tyramine is a byproduct of Tyrosine metabolism by MAO in the liver Typically it will have low bioavailability due to extensive firstpass effect in the liver If the patient is taking a MOA inhibitor, Tyramine accumulates in the bloodstream;If you are taking an MAOI and develop symptoms of a hypertensive crisis (especially after eating a hightyramine food) call 911 or go to your local emergency room A Word From Verywell If your doctor prescribes an MAOI for you, ask them for a complete list of
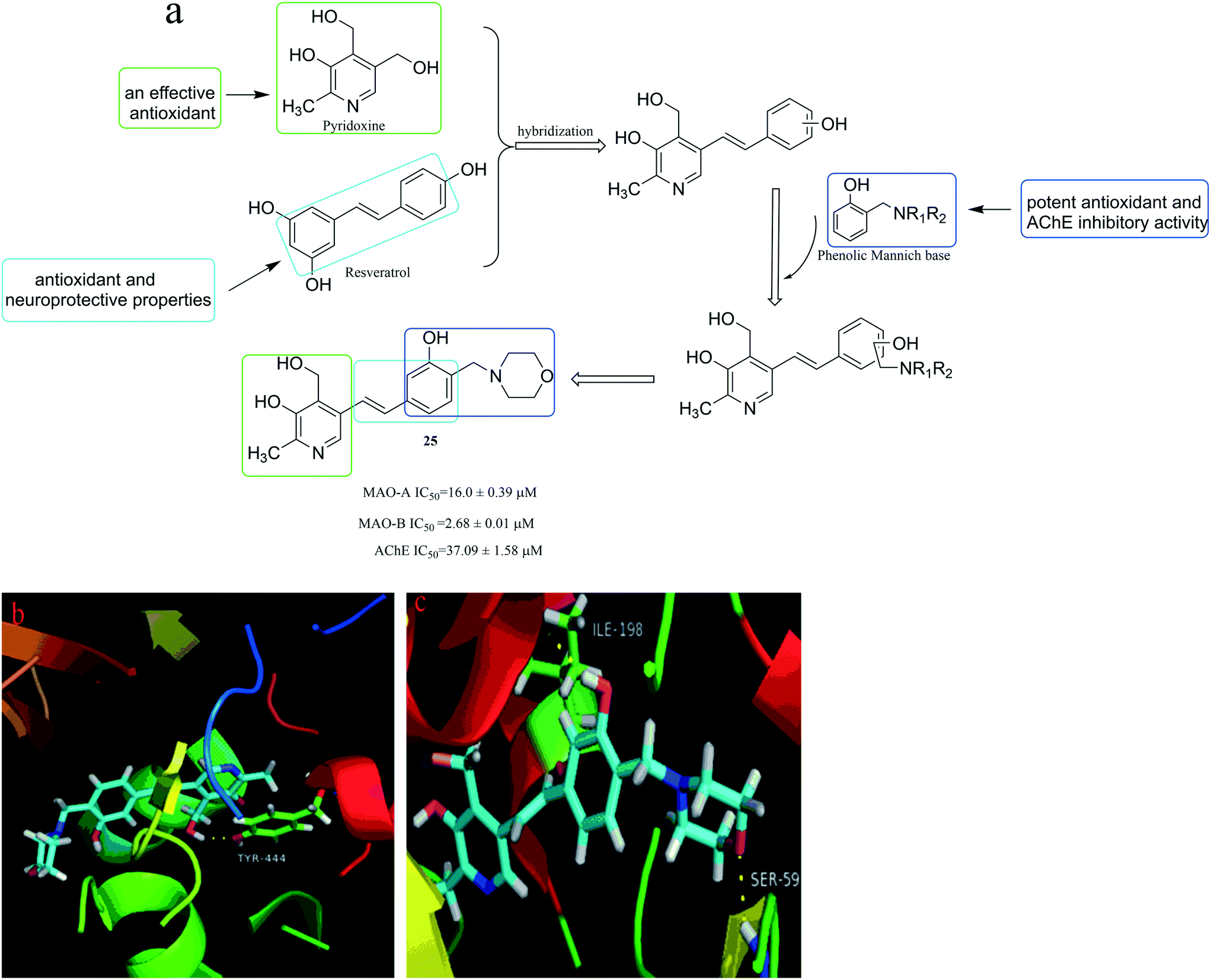


Discovery Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors By Medicinal Chemistry Approaches Medchemcomm Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C8mdc



Curcumin And The Mao Inhibitor Cheese Effect From Induced Info
2312 · To prevent adverse reactions such as severe headache, tachycardia and hypertension in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medications by restricting the tyramine content of the diet



Selegiline Wikipedia



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Transdermal Delivery System Of Mao Inhibitors Psychiatrist Com



What Is The Tyramine Reaction And How Do Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maois Cause It Youtube



Tyramine Wikipedia



Newly Developed Reversible Mao B Inhibitor Circumvents The Shortcomings Of Irreversible Inhibitors In Alzheimer S Disease Science Advances
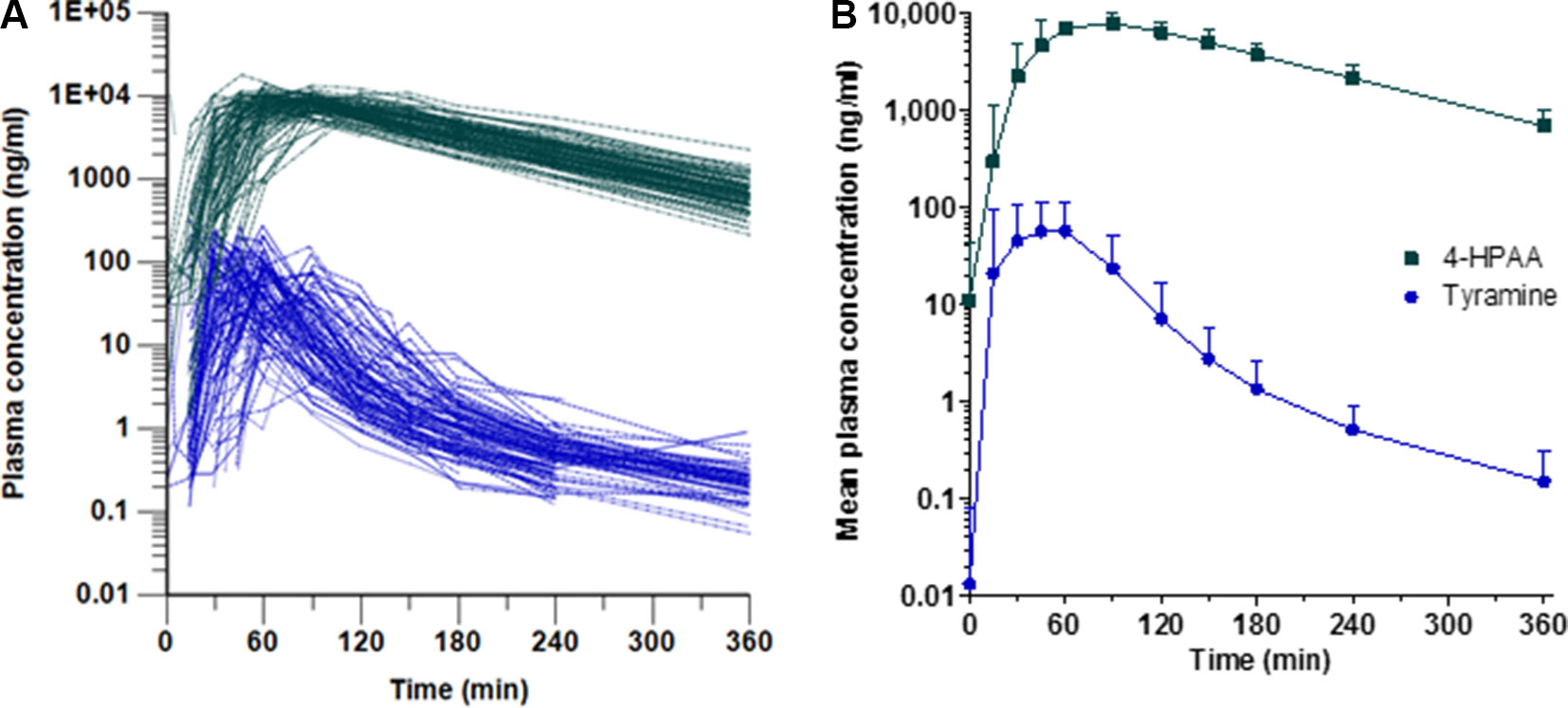


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Sembragiline A Novel Selective Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitor For The Treatment Of Alzheimer S Disease Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics



Tyramine And Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com
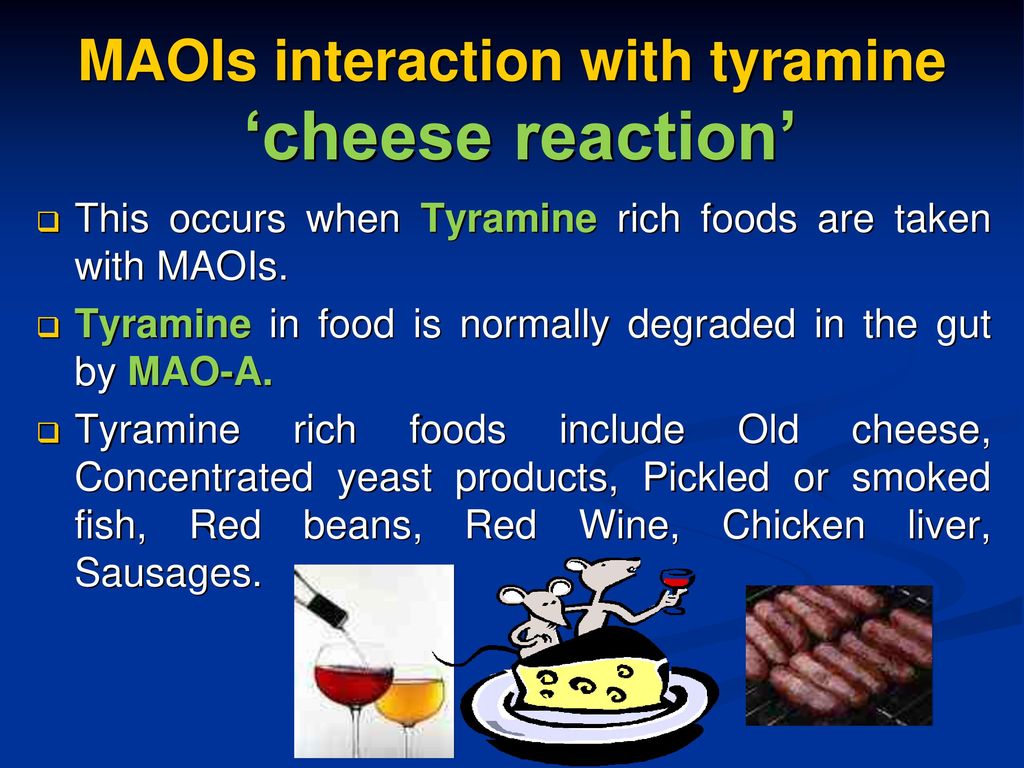


Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download
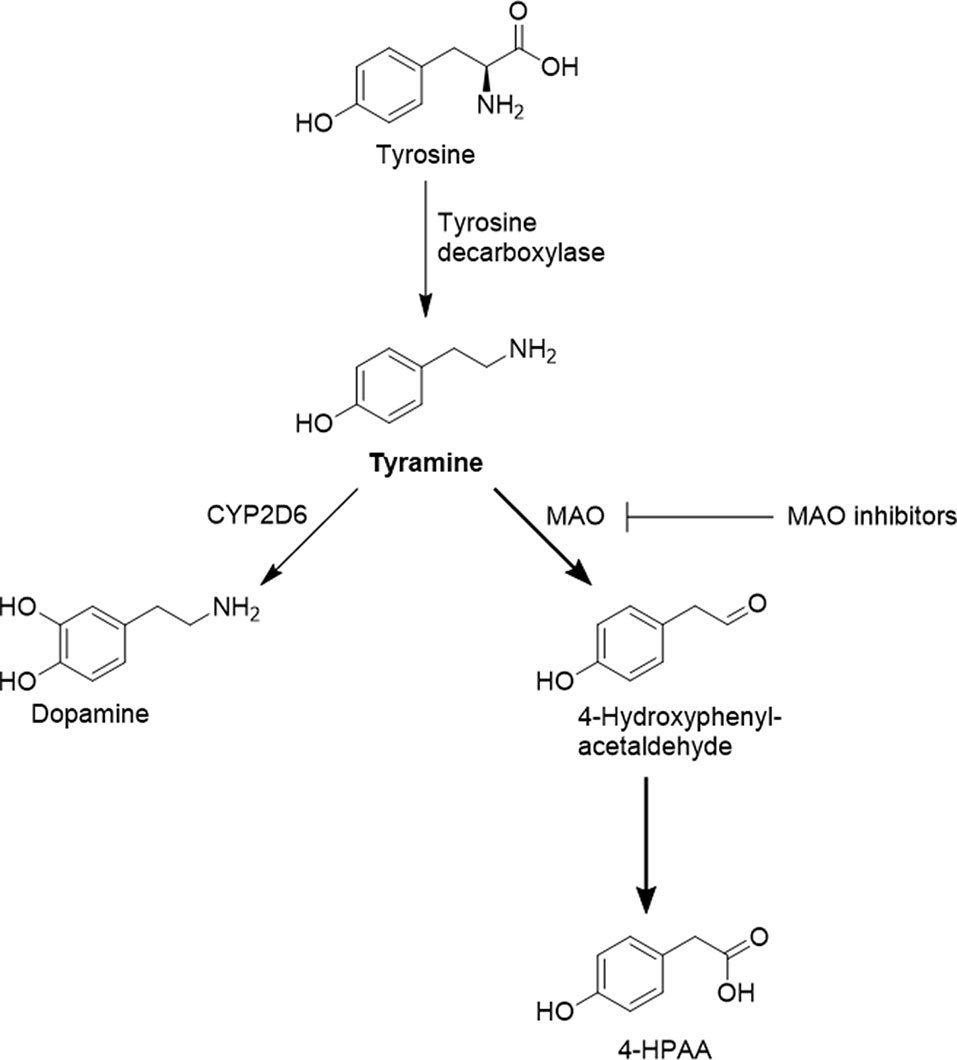


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry
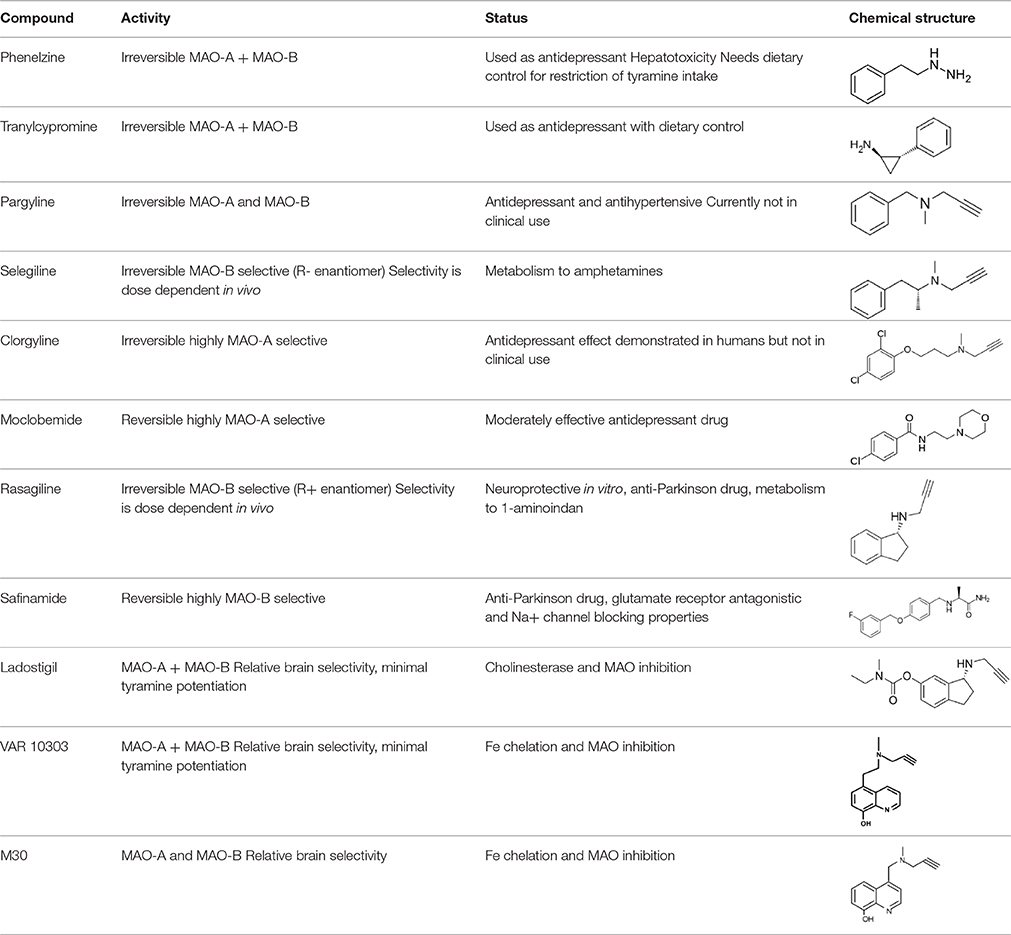


Frontiers Inhibitors Of Mao A And Mao B In Psychiatry And Neurology Pharmacology
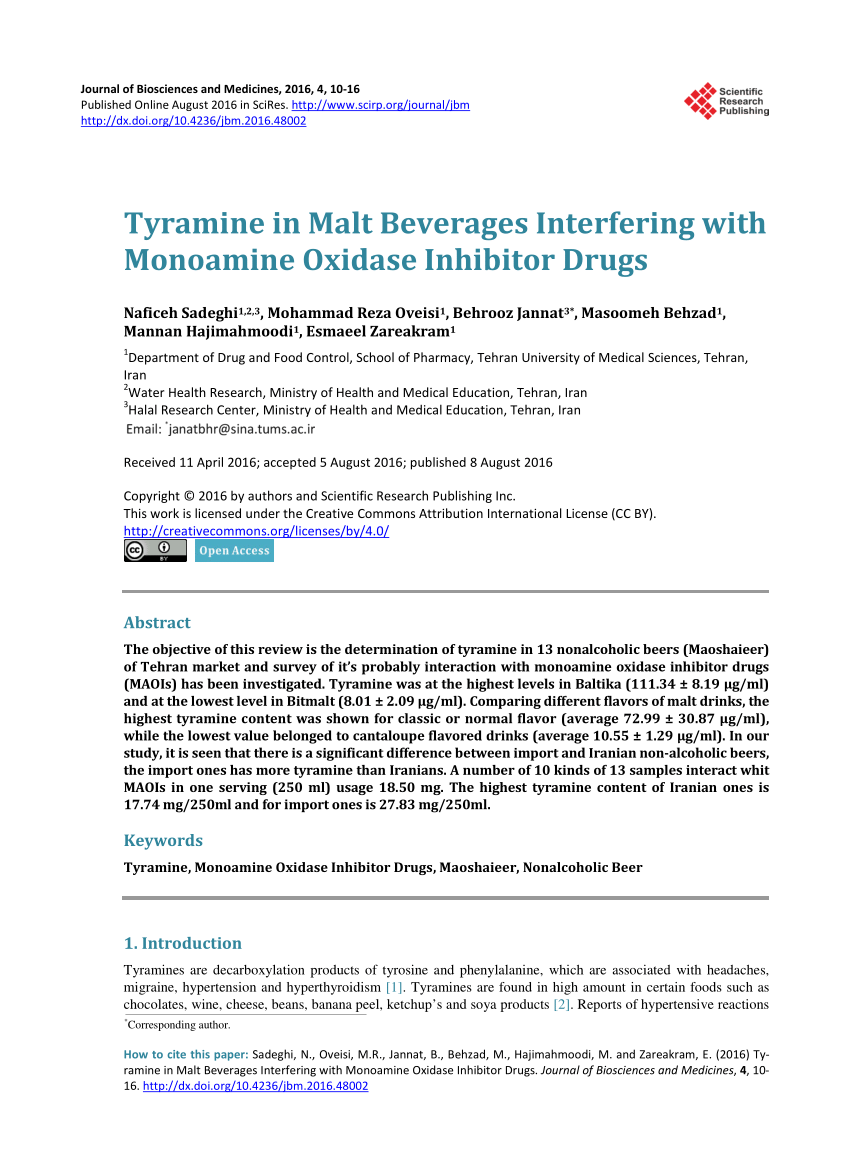


Pdf Tyramine In Malt Beverages Interfering With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drugs



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology
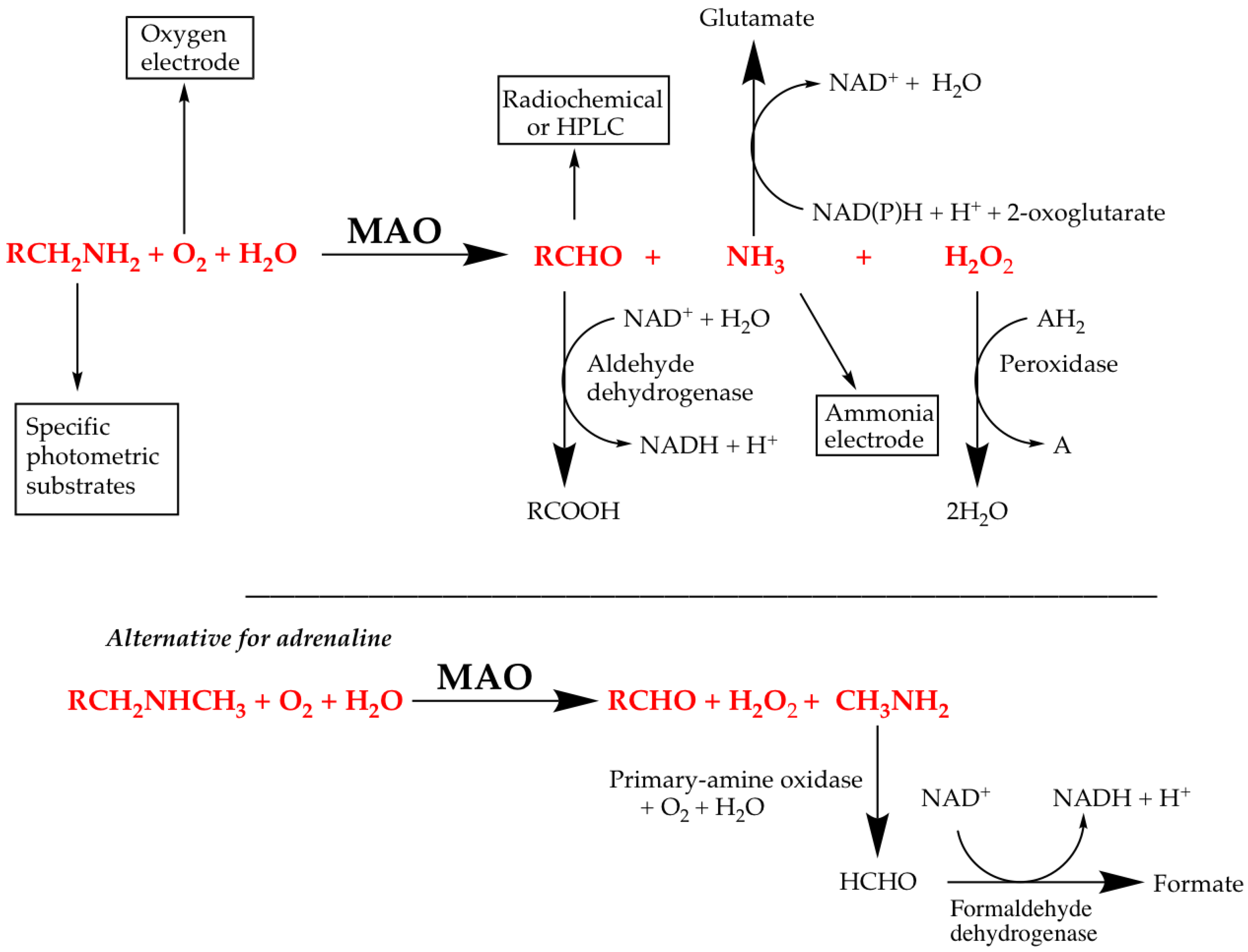


Molecules Free Full Text Assessment Of Enzyme Inhibition A Review With Examples From The Development Of Monoamine Oxidase And Cholinesterase Inhibitory Drugs Html



Well Known Side Effects Of Antidepressants You Should Be Aware Of
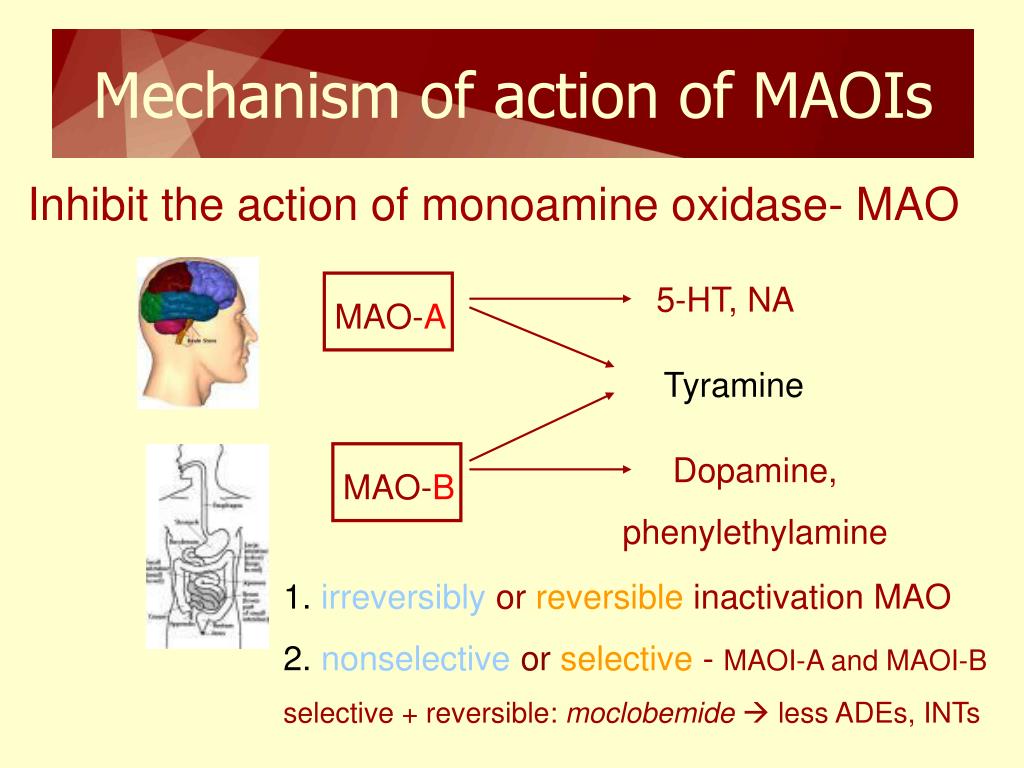


Ppt Pharmacology Section 10 Antidepressants And Mood Stabilizing Drugs Powerpoint Presentation Id



Maoi Drugs News



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
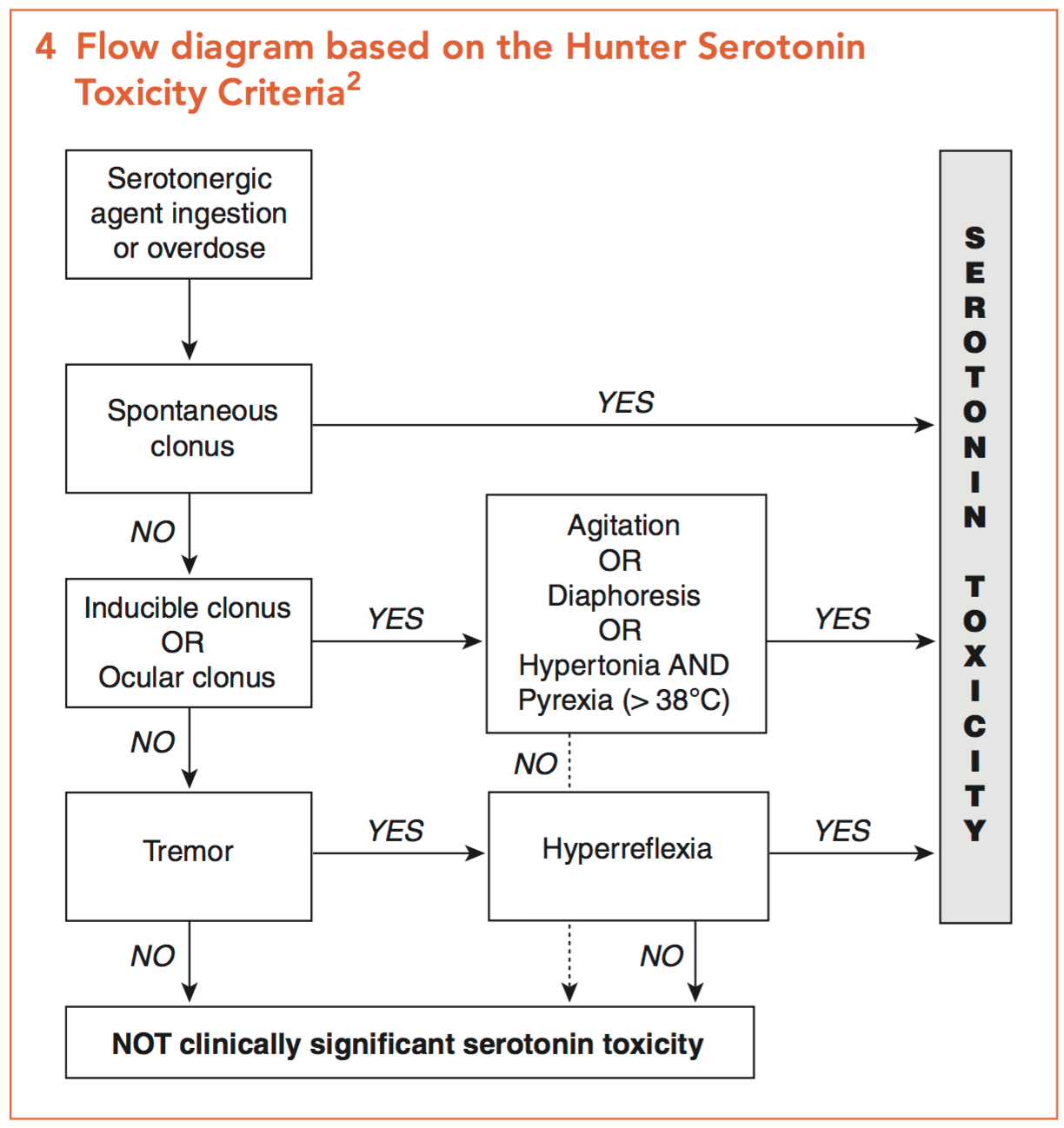


Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Relics Reconsidered Psychiatric Annals
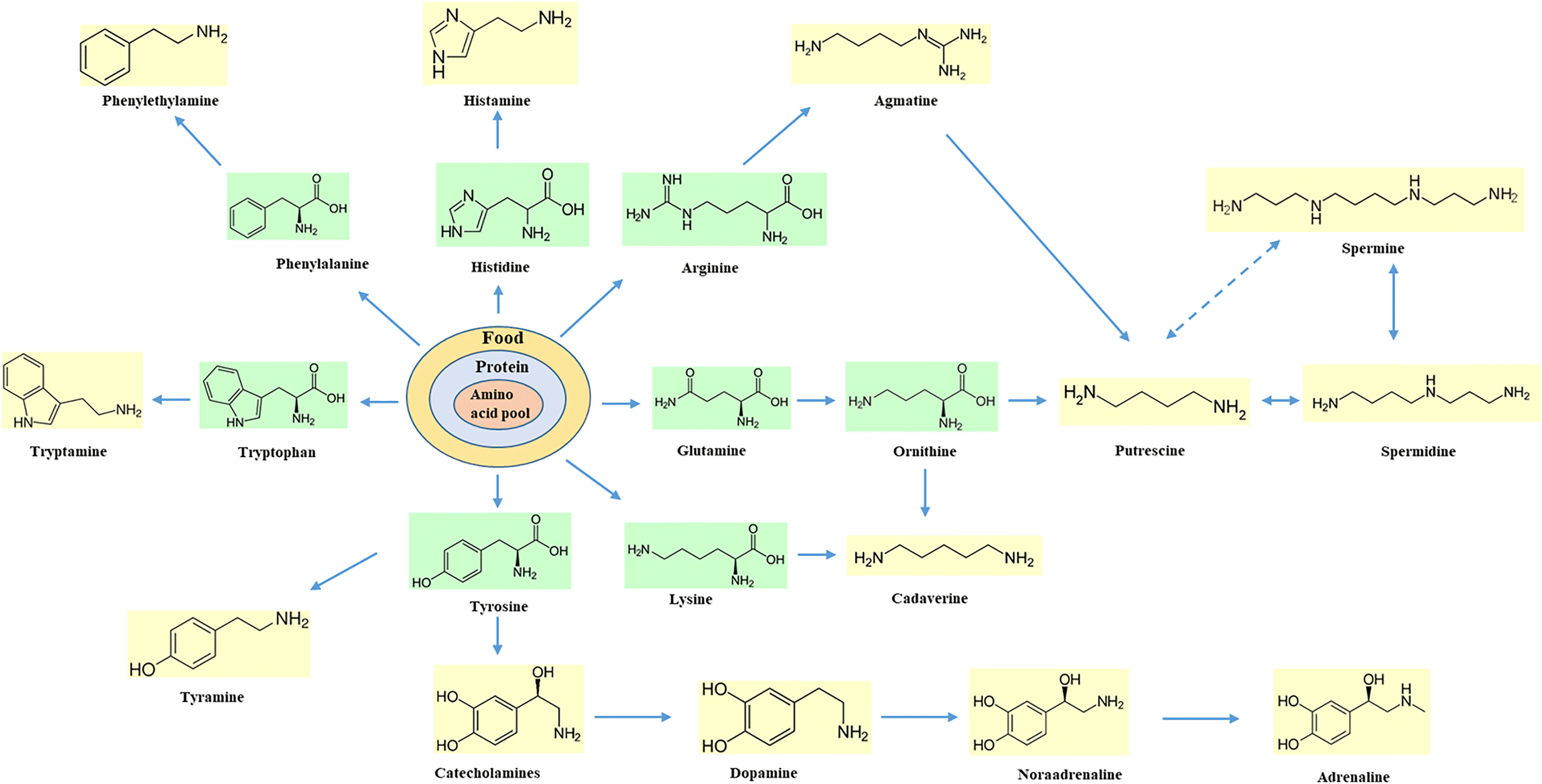


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039
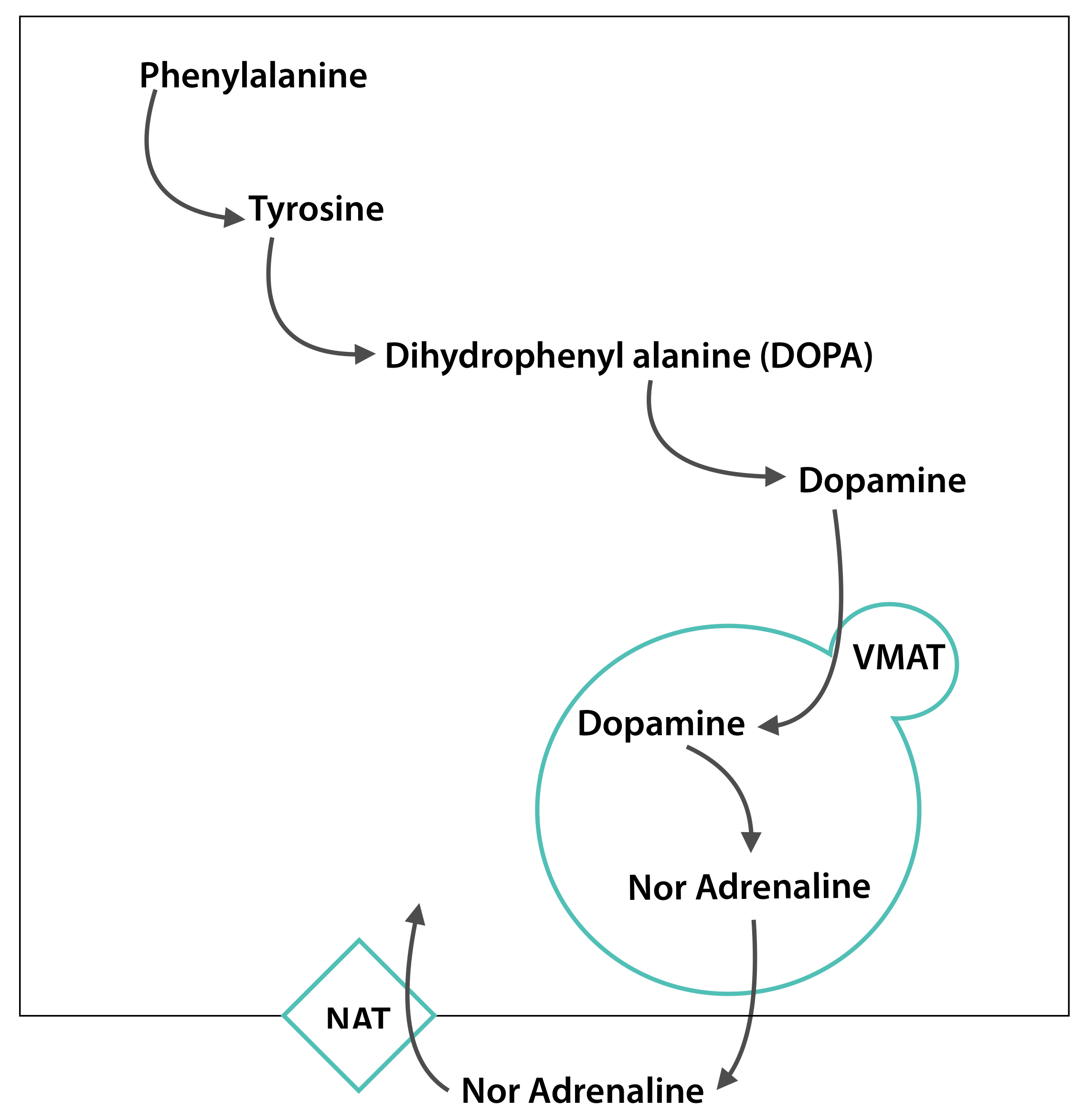


Death By Chocolate The Cheese Reaction Firstclass



Antidepressants Vaughan Asburys General Ophthalmology 17th Ed



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions
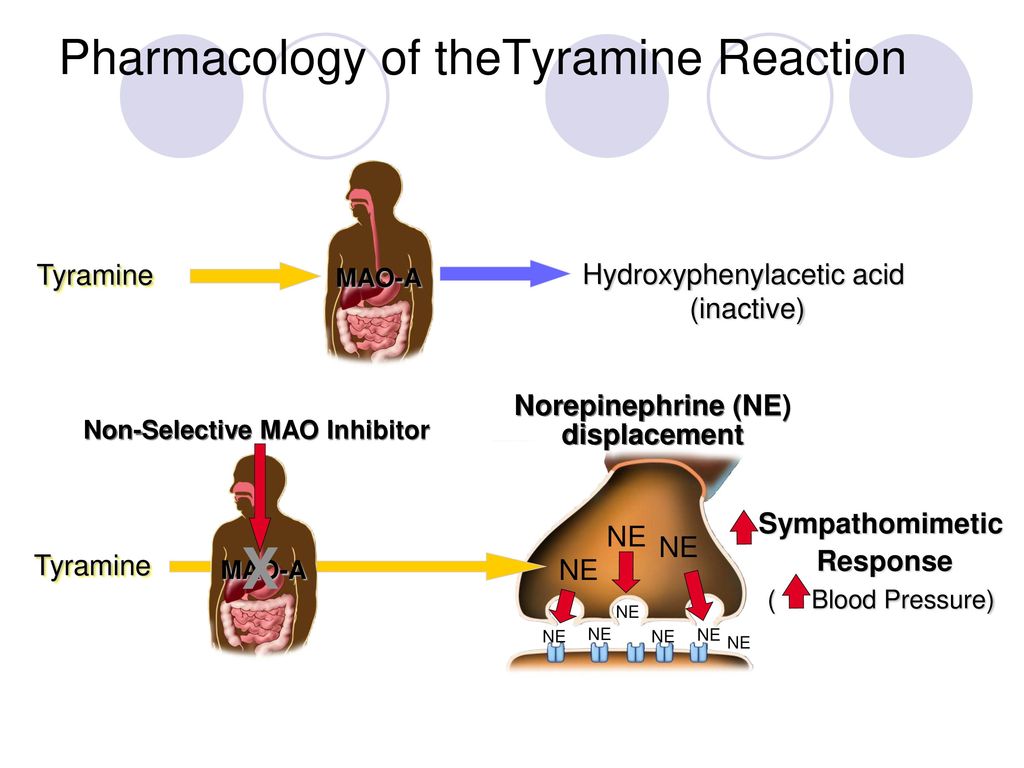


Antidepressants Drugs Which Can Elevate Mood Mood Elevators Ppt Download
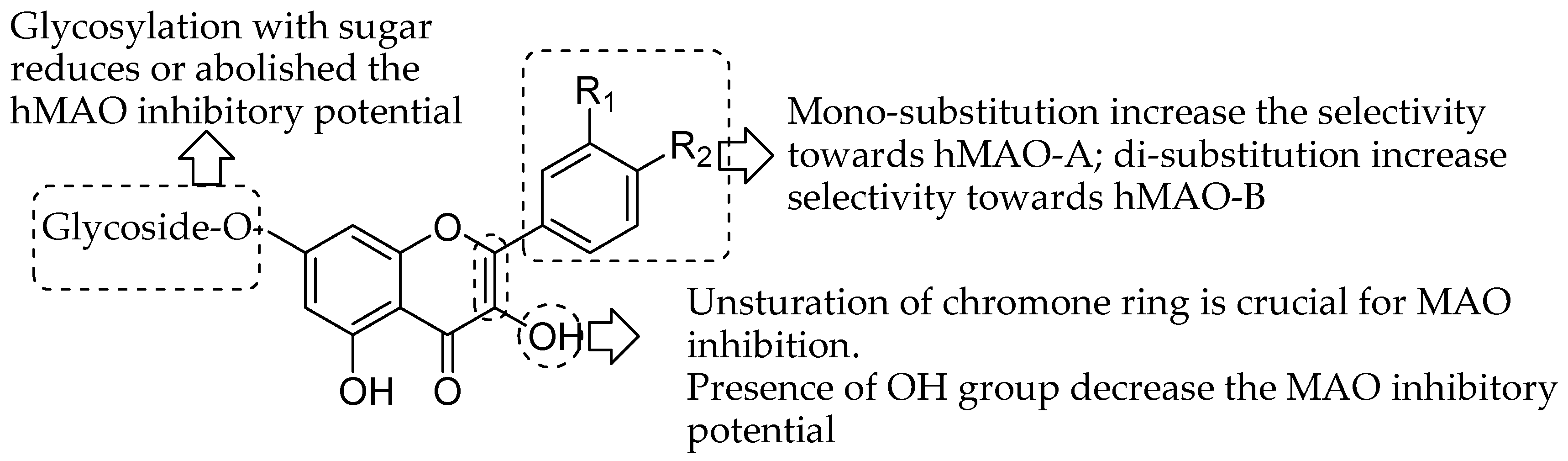


Molecules Free Full Text Quercetin And Related Chromenone Derivatives As Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Targeting Neurological And Mental Disorders Html
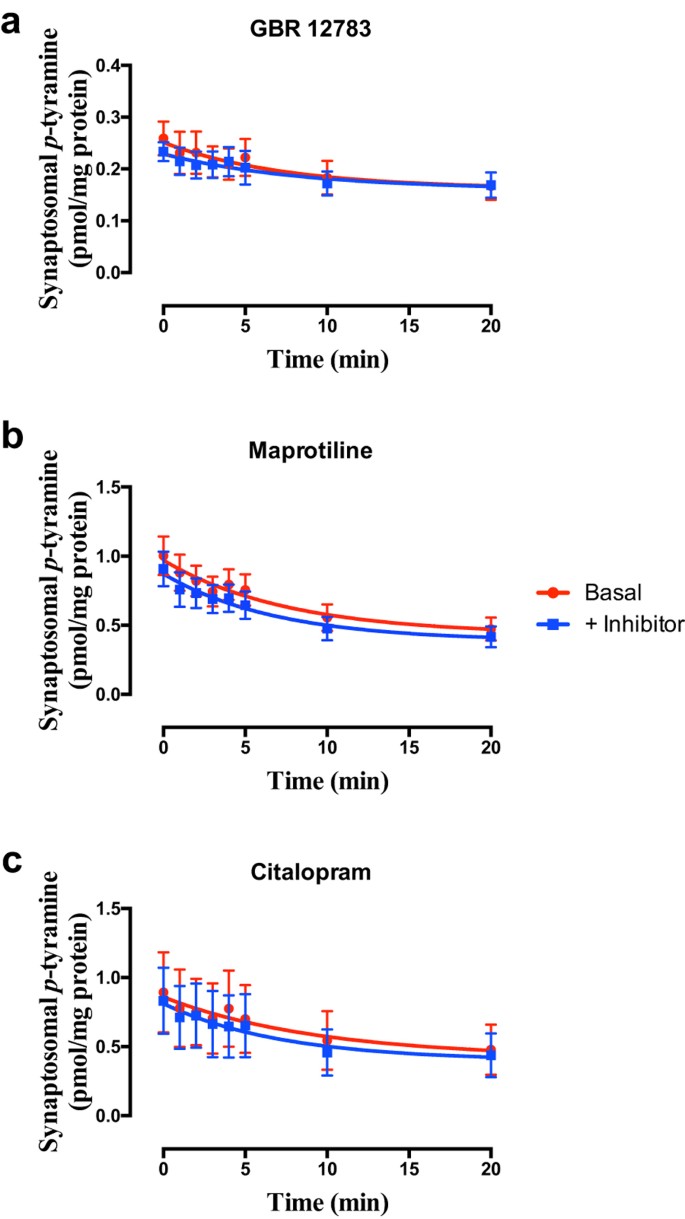


Pharmacological Characterization Of A High Affinity P Tyramine Transporter In Rat Brain Synaptosomes Scientific Reports



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download



Design Synthesis Molecular Modelling And In Vitro Screening Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities Of Novel Quinazolyl Hydrazine Derivatives Royal Society Open Science



Cheese Reaction Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com
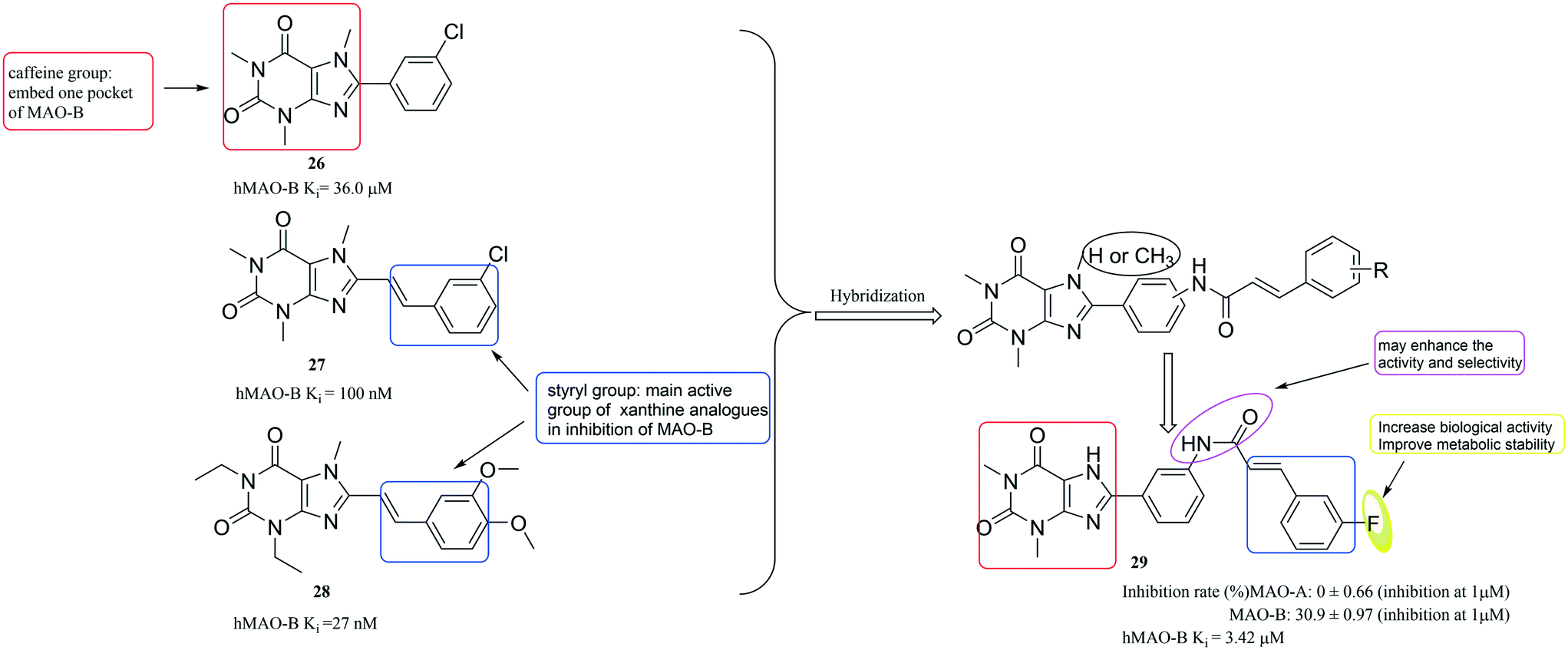


Discovery Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors By Medicinal Chemistry Approaches Medchemcomm Rsc Publishing



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Tyramine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Maois Diet High Tyramine Foods May Trigger Dangerous Side Effects



Antidepressants Vaughan Asburys General Ophthalmology 17th Ed



Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



Pdf Much Ado About Nothing Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Drug Interactions And Dietary Tyramine



Pdf Mao Inhibitors Risks Benefits And Lore Semantic Scholar



Transdermal Delivery System Of Mao Inhibitors Psychiatrist Com
/GettyImages-746275147-5b0b3813fa6bcc0037205902.jpg)


Dietary Precautions While Taking Maois



Pdf Oral Tyramine Pressor Test And The Safety Of Mao Inhibitor Drugs



Pdf Tyramine Potentiation During Treatment With Mao Inhibitors Brofaromine And Moclobemide Vs Irreversible Inhibitors



Tyramine To Norepinephrine Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



What Is Cheese Reaction Mao I Non Selective In Pharmacology Youtube



Maois Diet Full Amino Acid Foods



Newly Developed Reversible Mao B Inhibitor Circumvents The Shortcomings Of Irreversible Inhibitors In Alzheimer S Disease Science Advances



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download


Mao B Inhibitor Introduction



Tyramine Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia



Maoi



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Maoi



Tyramine Reaction Page 4 Line 17qq Com


